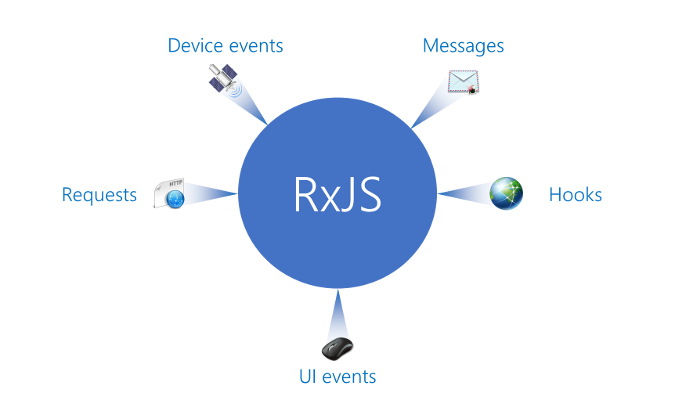
Rx更进一步
借用Jay phelps在Youtube上介绍Rx十分精炼的总结,Rx = Lodash of Promise,在Node或是前端,处理异步一直是一个麻烦的事情,于是就有了各种各样的异步解决方案,callback,exent,Promise,generate,async/await现在我们又有了Rx。
异步解决方案
以读写文件为例子,看看异步处理方案的演进
callback
1
2
3
4
| fs.readFile('test.txt', (err, data) => {
if (err) console.log(err);
console.log(data)
})
|
event
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| let readStream = fs.createReadStream('test.txt');
readStream.on('open', (data) => {
console.log(data)
})
readStream.close('close', () => {
console.log('closed')
})
|
Promise && async/await
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| function readFilePromise(path) {
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
fs.readFile(path, (err, data) => {
if(err) {
rej(err)
}
res(data)
})
})
}
readFilePromise('test.txt').then(data => {console.log(data)})
async function result() {
await readFilePromise('test.txt');
}
|
Generator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function run(gen) {
var iter = gen(function (err, data) {
if (err) { iter.throw(err); }
return iter.next(data);
});
iter.next();
}
run(function* (resume) {
var contents = yield require('fs').readFile('test.txt', resume);
console.log(contents);
});
|
Rx
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
let readFileAsObservable = Observable.bindNodeCallback((
path: string,
encoding: string,
callback: (error: Error, buffer: Buffer) => void
) => fs.readFile(path, encoding, callback));
let result = readFileAsObservable('./test.txt', 'utf8');
result.subscribe(
buffer => console.log(buffer.toString()),
error => console.error(error)
);
|
仅仅是的文件,就有各种风格各异的解决方式,又都有各自的缺点,callback hell,Generator的死板, Promise也只是改变了callback的形式,async/await倒是很直观的一种表达,又因为其简便易用会导致人们的滥用。Rx在代码量大的情况下的可读性不是很好,又有一定的学习成本,所以没有完美的方案,只有适合的方案。
如果在读文件的基础上加一些条件,比如读两个文件,而第二个文件又依赖于第一个文件的话
1
2
3
4
5
| const file1$ = readFileAsObservable('file1.txt');
const file2$ = readFileAsObservable('file2.txt');
file1$.concatMap(data => file2).subscribe(data ={
console.log(data)
})
|
一个handbook的例子很好的说明了Rx的特点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| import { of } from 'rxjs/observable/of';
import { concatMap, delay, mergeMap } from 'rxjs/operators';
// 发出延迟值
const source = of(2000, 1000);
// 将内部 observable 映射成 source,当前一个完成时发出结果并订阅下一个
const example = source.pipe(
concatMap(val => of(`Delayed by: ${val}ms`).pipe(delay(val)))
);
// 输出: With concatMap: Delayed by: 2000ms, With concatMap: Delayed by: 1000ms
const subscribe = example.subscribe(val =>
console.log(`With concatMap: ${val}`)
);
// 展示 concatMap 和 mergeMap 之间的区别
const mergeMapExample = source
.pipe(
// 只是为了确保 meregeMap 的日志晚于 concatMap 示例
delay(5000),
mergeMap(val => of(`Delayed by: ${val}ms`).pipe(delay(val)))
)
.subscribe(val => console.log(`With mergeMap: ${val}`));
|
广播在PostMessage的情况下实现多页面的广播
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import { interval } from 'rxjs/observable/interval';
import { Subject } from 'rxjs/Subject';
import { take, tap, multicast, mapTo } from 'rxjs/operators';
// 每2秒发出值并只取前5个
const source = interval(2000).pipe(take(5));
const example = source.pipe(
// 因为我们在下面进行了多播,所以副作用只会调用一次
tap(() => console.log('Side Effect #1')),
mapTo('Result!')
);
// 使用 subject 订阅 source 需要调用 connect() 方法
const multi = example.pipe(multicast(() => new Subject()));
/*
多个订阅者会共享 source
输出:
"Side Effect #1"
"Result!"
"Result!"
...
*/
const subscriberOne = multi.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
const subscriberTwo = multi.subscribe(val => console.log(val));
// 使用 subject 订阅 source
multi.connect();
|
handBook 上计数器的实现方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| //
const takeUntilFunc = (Range, current) => {
if (Range > current) {
return val => val <= Range;
} else {
return val => val >= Range;
}
};
const positiveOrNegative = (endRange, currentNumber) => {
if (endRange > currentNumber) {
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
};
const renderUpdate = id => content => (document.getElementById(id).innerHTML = content);
const input = document.getElementById('range');
const updateButton = document.getElementById('update');
const subscription = (function(currentNumber) {
return fromEvent(updateButton, 'click').pipe(
map(_ => parseInt(input.value)),
switchMap(endRange => {
return timer(0, 20).pipe(
mapTo(positiveOrNegative(endRange, currentNumber)),
startWith(currentNumber),
scan((acc, curr) => acc + curr),
takeWhile(takeUntilFunc(endRange, currentNumber));
)
}),
tap(v => (currentNumber = v)),
startWith(currentNumber)
)
.subscribe(renderUpdate('display'));
})(0);
|
受Rx的影响更有cycle.js提出的反应式编程虽然这个概念并没有大火,但依然提出了一个新的思考
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| // cycle编写的counter
// 让DOM操作又了Stream的加持。。
function main(sources) {
const decrement$ = sources.DOM
.select('.decrement').events('click').mapTo(-1);
const increment$ = sources.DOM
.select('.increment').events('click').mapTo(+1);
const action$ = xstream.merge(decrement$, increment$);
const count$ = action$.fold((x, y) => x + y, 0);
const vtree$ = count$.map(count =>
div([
button('.decrement', 'Decrement'),
button('.increment', 'Increment'),
p('Counter: ' + count)
])
);
return { DOM: vtree$ };
}
|
总之Rx是一支很成熟的解决方案,尤其是应对复杂度高的的场景的时候越能体现其价值。
